AGP SLOT
 The Accelerated Graphic Port (AGP) was developed by
Intel so that the video card would have direct access with memory. This would create a higher performance of graphic capibilities.
The Accelerated Graphic Port (AGP) was developed by
Intel so that the video card would have direct access with memory. This would create a higher performance of graphic capibilities.
BIOS Battery

The BIOS Battery is used to supply power to the BIOS or EEPROM. It also supplies power to
the system clock (The system clock is the pace keeper for the components on the motherboard).
Chipset
 The chipset is the heart of the motherboard. It controls the flow of data over the motherboard.
There is usually a Northbridge Chipset (AGP Chipset) and a Southbridge Chipset (PCI Chipset). Each chipset enhances the performance and capabilities of the AGP and PCI as well as the entire motherboard.
The chipset is the heart of the motherboard. It controls the flow of data over the motherboard.
There is usually a Northbridge Chipset (AGP Chipset) and a Southbridge Chipset (PCI Chipset). Each chipset enhances the performance and capabilities of the AGP and PCI as well as the entire motherboard.
ASUS CPU

The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the motherboard. The CPU is the most important component on the motherboard. The CPU or otherwise called a Processor has two important components. One is the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) which performs arithmetic and logical operations. The other component is the Control Unit which gets instructions from memory then executes them. It also uses the ALU when it has to. This ASUS CPU is an older type of CPU and resembles a Nintendo Cartridge.
The Common PC CPU and Socket

The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the motherboard. The CPU is the most important component on the motherboard. The CPU or otherwise called a Processor has two important components. One is the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) which performs arithmetic and logical operations. The other component is the Control Unit which gets instructions from memory then executes them. It also uses the ALU when it has to. This is what the newer and most common CPUs look like as well as a type of slot it uses. These type of CPUs are much faster then the older Nintendo type of CPUs like the ASUS CPU.

Fan

The fan on the motherboard has the same purpose as any other fan, to cool something. There is always a fan on the motherboard to cool the CPU since the CPU does generates a lot of heat. Fans are also located in other spots on the motherboard that needs cooling.
Floppy
 A wide, thin ribbon like cable is used to connect the floppy drive to the motherboard. Every type of computer no matter of age or manufacturer comes with a floppy drive. It is the most basic method of storing data, most commonly 1.44 MB.
A wide, thin ribbon like cable is used to connect the floppy drive to the motherboard. Every type of computer no matter of age or manufacturer comes with a floppy drive. It is the most basic method of storing data, most commonly 1.44 MB.

Hardware Monitoring Chip

A hardware monitoring chip monitors the voltages, temperatures and fan speeds on the motherboard.
IDE Slots

An Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) slot is a place for storage devices like the hard drive
or CD-ROM drive to connect to the motherboard.
ISA Slots

An Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slot is an older type of technology used to connect expansion cards such as a modem or sound card to the motherboard.
PCI Slots
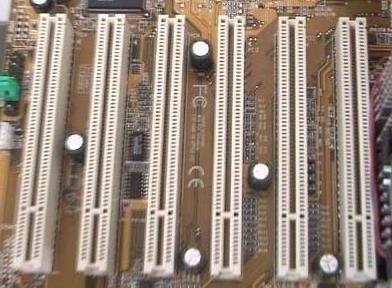
A Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slot performs the same fuction as an ISA slot, it connects expansion cards to the motherboard. The PCI slot is a newer technology that is much faster than the ISA slot.
Ports
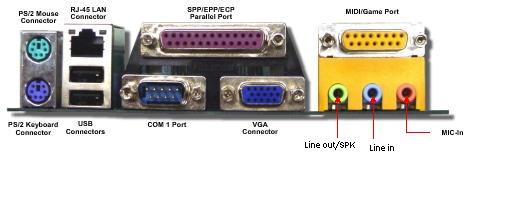
A port is a place to connect most of your external devices such as your keyboard or printer. There are many different types of connectors for each different device. Your keyboard would connect into a circular PS/2 connector whereas your printer could connect to a rectangular USB connector.
Power

Your computer wouldn't work if it didn't have power, so a power source has to be connected to your motherboard. Older motherboards (AT motherboards) used two cables (a P8 and P9
connector) that plugged into the motherboard. Newer motherboards (ATX motherboards) use a P1 connector to connect to the motherboard.

Progammable Flash EEPROM

Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM) is a type of memory that can store data even when the main power is off. It uses the BIOS Battery as its power source to allow it to store the data. Unlike like ROM (Read-Only Memory), EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed without replacing the chip.
RAM
Dimm slots and Dimm

 Random Access Memory (RAM) is a temporary place to store data but is erased once the main power is turned off. The data is stored on chips called Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) which can be inserted into DIMM slots located on the motherboard.
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a temporary place to store data but is erased once the main power is turned off. The data is stored on chips called Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) which can be inserted into DIMM slots located on the motherboard.
SB-Link

An SB-Link is a connector that links the ISA bus to the PCI sound card and guides the signal between the two. The older ISA bus contains some signals that the newer PCI bus doesn't.
An example would be an older game that needs direct access to signals from the ISA bus. (A bus is the term used for the lines that data, instructions and power travel on.)
Super Multi-I/O Chip

The Super Multi-I/O chip is used to control the signals between Input/Output (I/O) devices and the motherboard. This allows such Input/Output (I/O) devices like printers and keyboards to communicate with the motherboard.
Wake-On-LAN Connector
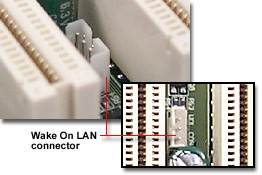
In order to connect to a network you must have a Network Interface Card (NIC Card) which insert into PCI slots. The Wake-On-LAN Connector connects to a NIC Card and allows the computer to power on if the right signal is sent across the network.